Dear All
It is our pleasure to share our greetings for DASHAIN with you all
During the month of Kartik in the Bikram Sambat calendar (late September and early October), the Nepalese people indulge in the biggest festival of the year, Dashain. Dashain is the longest and the most auspicious festival in the Nepalese annual calendar, celebrated by Nepalese of all caste and creed throughout the country. The fifteen days of celebration occurs during the bright lunar fortnight ending on the day of the full moon. Thorough out the kingdom of Nepal the goddess Durga in all her manifestations are worshiped with innumerable pujas, abundant offerings and thousands of animal sacrifices for the ritual holy bathing, thus drenching the goddess for days in blood.
Dashain commemorates a great victory of the gods over the wicked demons. One of the victory stories told is the Ramayan, where the lord Ram after a big struggle slaughtered Ravana, the fiendish king of demons. It is said that lord Ram was successful in the battle only when goddess Durga was evoked. The main celebration glorifies the triumph of good over evil and is symbolized by goddess Durga slaying the terrible demon Mahisasur, who terrorised the earth in the guise of a brutal water buffalo. The first nine days signify the nine days of ferrous battle between goddess Durga and the demon Mahisasur. The tenth day is the day when Mahisasur was slain and the last five days symbolise the celebration of the victory with the blessing of the goddess. Dashain is celebrated with great rejoice, and goddess Durga is worshiped throughout the kingdom as the divine mother goddess.
In preparation for Dashain every home is cleansed and beautifully decorated, painted as an invitation to the mother goddess, so that she may visit and bless the house with good fortune. During this time the reunion of distant and nearby relatives occur in every household. The market is filled with shoppers seeking new clothing, gifts, luxuries and enormous supplies of temple offering for the gods, as well as foodstuffs for the family feasting. Thousands of sheep, goats, ducks, chicken and water buffalo are prepared for the great slaughter. All types of organisations are closed for ten to fifteen days. Labourers are almost impossible to find; from the poor to the rich, all enjoy the festive mood. Anywhere you go the aroma of ‘Vijaya Dashami’ is found.
The first nine days of Dashain are called nawa ratri when tantric rites are conducted. In Nepal the life force is embodied in the divine energy and power of the female, depicted as goddess Durga in her many forms. All goddess who emanated from goddess Durga are known as devis, each with different aspects and powers. In most mother goddess temples the deity is represented simply as a sacred Kalash, carved water jug or multiple handed goddess holding murderous weapons. During these nine days people pay their homage to the goddess. If she is properly worshiped and pleased good fortunes are on the way and if angered through neglect then misfortunes are around the corner. Mother goddess is the source of life and everything.
The first day of Dashain is called Ghatasthapana, which literally means pot establishing. On this day the kalash, (holy water vessel) symbolising goddess Durga often with her image embossed on the side is placed in the prayer room. The kalash is filled with holy water and covered with cowdung on to which seeds are sown. A small rectangular sand block is made and the kalash is put in the centre. The surrounding bed of sand is also seeded with grains. The ghatasthapana ritual is performed at a certain auspicious moment determined by the astrologers. At that particular moment the priest intones a welcome, requesting goddess Durga to bless the vessel with her presence.
The room where the kalash is established is called ‘Dashain Ghar’. Generally women are not allowed to enter the room where Dashain puja is being carried out. A priest or a household man worships the kalash everyday once in the morning and then in the evening. The kalash and the sand are sprinkled with holy water everyday and it is shielded from direct sunlight. By the tenth day, the seed will have grown to five or six inches long yellow grass. The sacred yellow grass is called ‘Jamara’. It is bestowed by the elders atop the heads of those younger to them during the last five days when tika is put on. The jamara is taken as a token of Goddess Durga as well as the elders blessing.
As days passes by regular rituals are observed till the seventh day. The seventh day is called ‘Fulpati’. On this day the jamara to be used by the royal household is brought from their ancestral royal house in Gorkha about a hundred and sixty nine kilometres away over the hills north west of the valley of Kathmandu. A parade is held in the Hanuman Dhoka Royal Palace. The fulpati, i.e. the procession bearing the jamara and other items necessary for the tika, is brought from Gorkha after a three day walk and most of the government officials are eagerly waiting for the fulpati parade to arrive at Rani Phokari in the afternoon. Rani Phokari area is filled with hundreds of government officials meticulously attired in the traditional formal dress.
In fulpati, the royal kalash filled with holy water, banana stalks, jamara and sugar cane tied with red cloth is carried by Brahmans from the ancestral royal house on a decorated palanquin under a gold tipped and embroidered umbrella, led by the military platoon of the royal priest. The government officials also join the fulpati parade. Whilst the fulpati parade is heading towards the old royal palace, His Majesty the King observes the ceremonies taking place in Tundikhel, the army parade ground in the center of the city. There a majestic display of the Royal Nepalese Army is held. Guns are fired and the entire valley echoes with the resonance sound of it.. The firing continues for ten to fifteen minutes to honour the fulpati. By the time the function ends the royal fulpati is already taken inside the Dashain ghar in Hanuman Dhoka Palace. With this the Dashain feasting starts.
The eighth day is called the ‘Maha Asthami’. The fervour of worship and sacrifice to Durga and Kali increases. On this day many orthodox Hindus will be fasting. Sacrifices are held in almost every house through out the day.. The night of the eighth day is called ‘Kal Ratri’, the dark night. Hundreds of goats, sheep and buffaloes are sacrificed at the mother goddess temples. In the darkness of the night Durga temples, army barracks, and old palaces all over Nepal hold sacrifices for the mother goddess. The sacrifice continues till dawn. The old palace in Basantapur Hanuman Dhoka, is active throughout the night with worships in almost every courtyard. While the puja is being carried out great feasts are held in the homes of common people where large amount of meat are consumed.
The ninth day is called ‘Nawami’. The Taleju temple at Hanuman Dhoka is opened for the public only once a year on this day. Thousands of people go and pay their respect to the goddess day. Temples of mother goddess are filled with people from dawn till dusk. On this day the official military sacrifices are held in the ‘Kot’ courtyard at Hanuman Dhoka. The government allows foreigners to witness this function so hundreds of tourists and diplomats eagerly gather here. Animals mostly black buffaloes are slaughtered by hundreds to honour Durga the goddess of victory and might and to seek her blessing. Military bands play war tunes, guns boom and officers with beautifully decorated medals in full uniform stand there. When the function ends the courtyard is filled ankle deep with blood. On this very day the god Vishwas Karma, the God of creativity is also worshiped. All factories, vehicles, any machinery instruments and anything from which we make a living are worshiped. We also give sacrifices to all moving machinery like cars, aeroplanes, trucks etc. to get the blessing from goddess Durga for protection for vehicles and their occupants against accidents during the year. The entire day is colourful.
The tenth day is the ‘Dashami’. On this day we take tika and jamara from our elders and receive their blessing. We visit our elders in their home and get tika from them while our younger ones come to our home to receive blessing from us. The importance of Dasain also lies in the fact that on this day family members from far off and distant relatives come for a visit as well as to receive tika from the head of the family. This function continues for four days. His Majesty also receives tika from the royal priests and then gives on tika to his loyal subjects. Thousands of loyal Nepalese people as well as foreigners also receive tika from His Majesty the King as this is said to be auspicious. After four days of rushing around and meeting your relatives Dashain ends on the full moon day, the fifteenth day. In the last day people stay at home and rest. The full moon day is also called ‘Kojagrata’ meaning ‘who is awake’. The Hindu goddess of wealth Laxmi is worshipped. On this day the goddess Laxmi is given an invitation to visit each and everyone.
After Dashain the nation settles back to normal. After receiving the blessing of goddess Durga, people are ready to work and acquire virtue, power and wealth. Dashain thus is not only the longest festival but also the most anticipated one among all the festivals of Nepal.
This is the information about Dashain ,
by Lila Nath Sapkota
Nepal today
Nepal has undergone major political changes in recent years. After a long time as a kingdom, the country has recently become a republic with a president as head of state. In April 2008, elections were held for a constituent assembly and the Maoist party became by far the largest party. The election was part of the peace process after the end of the Nepalese civil war in 2006, when negotiations between the Maoist guerrillas and the government led to a peace agreement.
In May 2008, the newly elected Constituent Assembly voted to abolish the monarchy, and in June, the Congress Party's candidate Ram Baran Yadav was elected as Nepal's first president. The Maoist Party did not receive a majority of its own in the assembly and therefore formed a coalition government with two other parties. Maoist party leader and former guerrilla leader Pushpa Kamal Dahal (also known as Prachanda) was appointed prime minister. Nepal has since tried to adapt to a new political system. In May 2009, a government crisis arose when the president overturned Prachanda's decision to dismiss the then army chief. The Maoists left the government and Madhav Kumar Nepal of the CPN-UML (United Marxist-Leninists) party formed a new coalition government consisting of 22 parties. The contradictions between the Maoist Party and the current government have created a very problematic political situation. Work on drafting a new constitution has been delayed and several important issues for the country's future remain unresolved.
The UN has a monitoring mission in Nepal, UNMIN (United Nations Mission in Nepal), whose current mandate extends until 23 January 2010. Sweden is currently contributing two military observers to the operation. The UN plays an important role in monitoring the peace and the question of the future of the Maoist soldiers is central to continued development. Nepal is one of the world's poorest countries and heavily dependent on aid. The current political situation is detrimental to the country's economic and social development.
Brief historical background
Nepal gained its current borders in the 18th century. From 1850 to 1950, a pro-British policy was pursued while Nepal's leaders sought to keep the country isolated from the outside world. Since then, Nepal has developed relations with primarily India. In the 1960s, the then king adopted a new constitution that strengthened the royal family's power over the country. In connection with reforms in 1990, Nepal transitioned to a multi-party system within the framework of a constitutional monarchy.
A widespread Maoist insurgency that began in 1996 marked the latter part of the 1990s and the early years of the 2000s. The political unrest led to King Gyanendra deposing the government in early 2005 and taking over executive power. After massive popular demonstrations, the king was forced to step back in the spring of 2006 and parliament was able to resume its work. The king's power was limited and negotiations began between the government and the Maoist guerrillas.
Source: Svenska Utrikesdepartementets hemsida 2010-09-28
http://www.sweden.gov.se/sb/d/2520/a/13981
http://www.forsvarsmakten.se/sv/Aktuellt/centralanyheter/Forsvarsmakten-vid-varldens-tak/
Nepal's Ambassador in Stockholm
The following four ambassadors presented their letters of credence to H.M. The King on Thursday, 29 January 2009. One of them was Nepal's new ambassador, Vijaykant Lal Karna, (laterally accredited to Copenhagen) who was born in 1959. He is a political scientist and has previously worked as an assistant professor at the University of Kritipur, Kathmandu. Since February 2008, he has been Nepal's ambassador in Copenhagen.
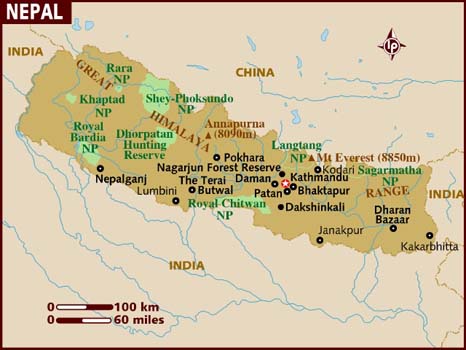
Nepal is about a quarter of the size of Sweden. At the very top of the north are the Himalayas with 8 of the world's 10 highest peaks. At the very south (above the name "India" in the picture), between Lumbini and Butwal, lies LWSTC. In the middle of the fertile farmland we find the school, built in the shape of a "U".


